Description
This Stream is so weird, looking something hidden here!!
Diffculity: Hard
Walkthrough
Challange is a wave file with high pitched noise, After examining file with usual tools (binwalk, exiftool, strings,..etc) we found nothing so we should dig deeper.
- Step 1: Analyze frames of wav file
- Using the following code we could get frame values
import wave, struct #import wave and struct library
wavefile = wave.open('data.wav', 'r') #read wave file
tmp=[] # create empty list with name tmp
length = wavefile.getnframes() # get number of frames in wave file
print(length) # print number of frames in wave file
for i in range(0, length): # create a loop to iterate through frames
wavedata = wavefile.readframes(1) # read one frame each loop
data = struct.unpack("<h", wavedata) # unpack data stored in wavedata buffer as integer
print(data[0]) #print frame value
- Quick look at values the negative signals are all equal to -1000 while positive signals differs from each other but if subtract 1000 from the positive value it will give us values from 0 to 255 so it may be characters
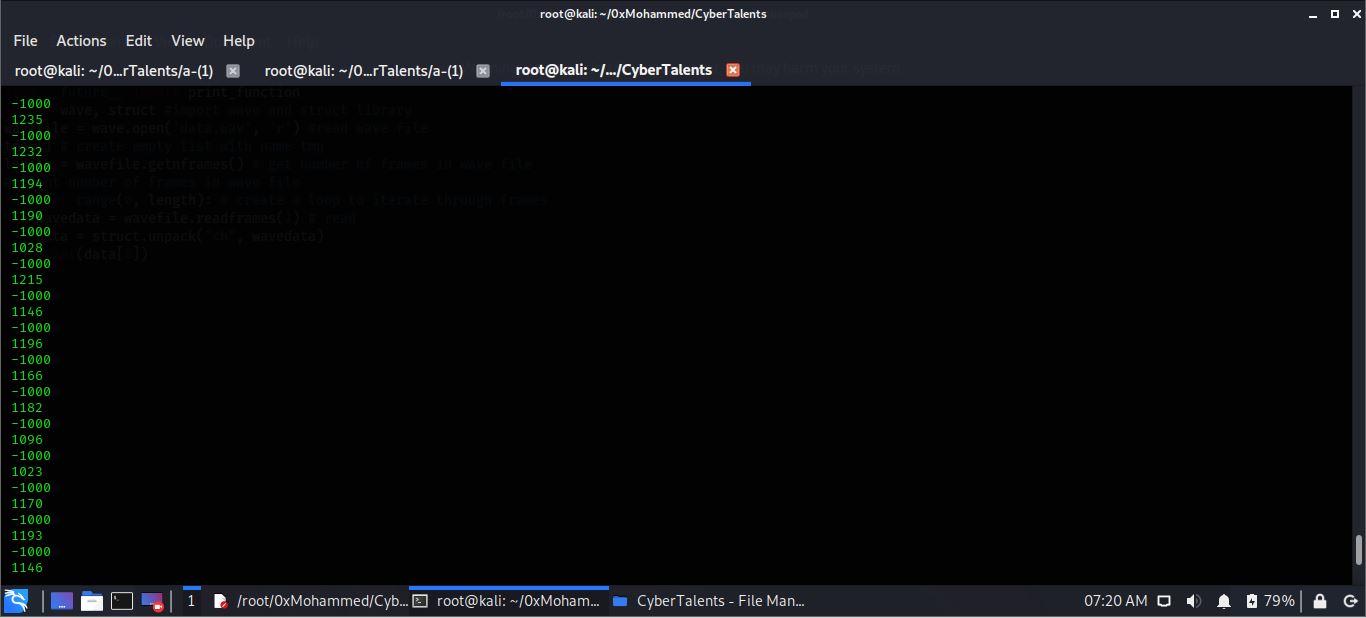
- Optimize the code to remove negative values -> subtract 1000 from positive values -> convert values to character -> redirect output to file. Remeber to use python2 for more details search for the difference between chr() in python2 and python3
from __future__ import print_function
import wave, struct
wavefile = wave.open('data.wav', 'r')
tmp=[]
length = wavefile.getnframes()
print(length)
for i in range(0, length):
wavedata = wavefile.readframes(1)
data = struct.unpack("<h", wavedata)
if data[0] > 0: #check if all values are positive
print(chr(data[0]-1000), end="") #subtract 1000 from positive values and convert to chr, and remove new line
- Step 2: Analyze output from code
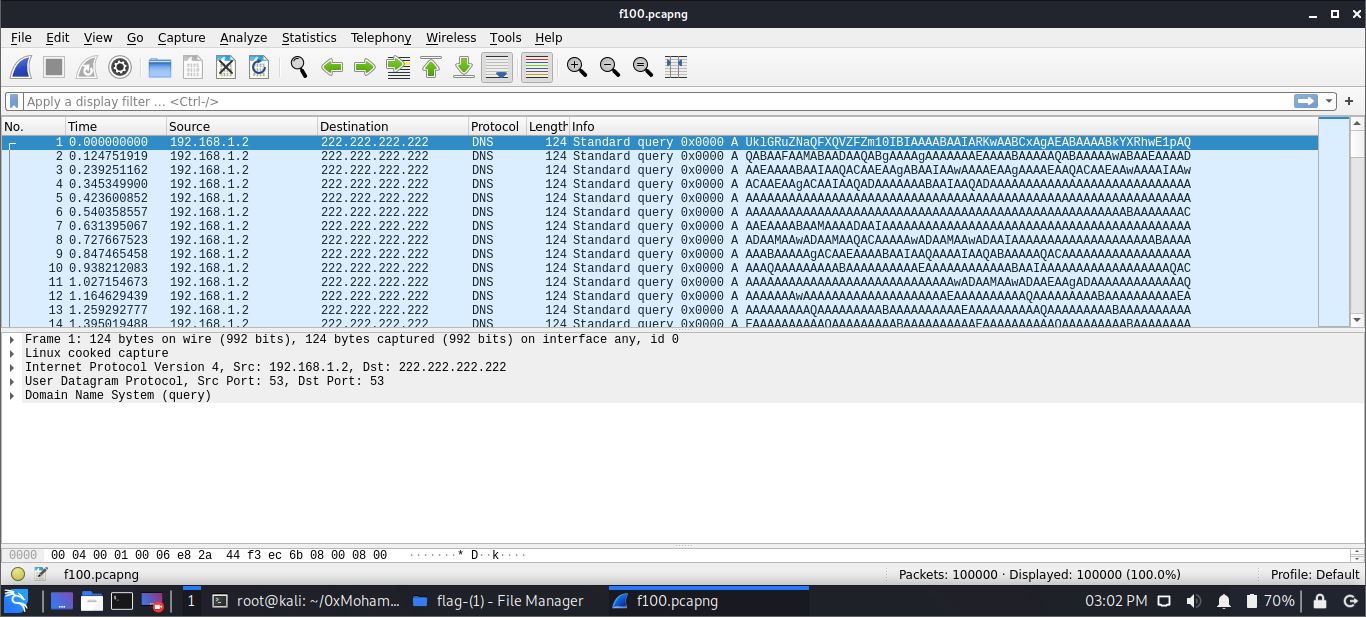
start with running strings utility but returns nothing usefull, after looking at file it’s icon turned into compressed file icon, running file utility on the file returns it is a gz compressed file, uncompress it give us 5 different packets f100, f200, f300, f400, f500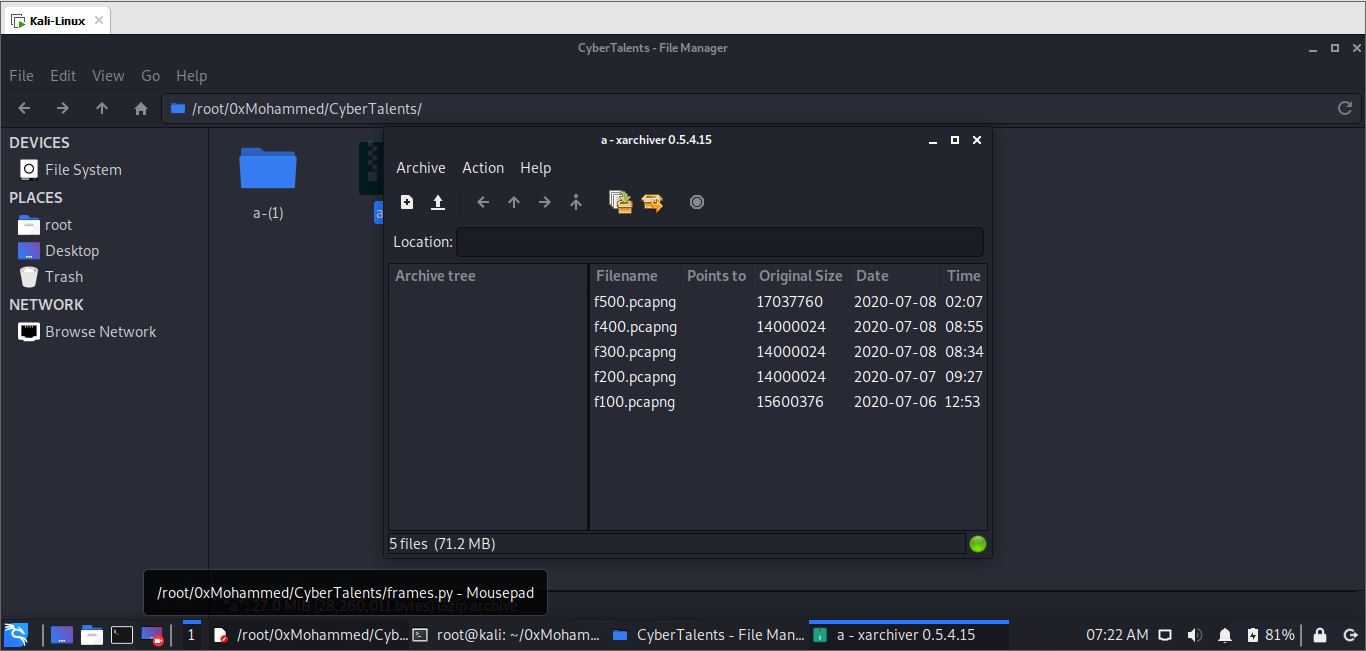
- Step 3: Analyzing packets
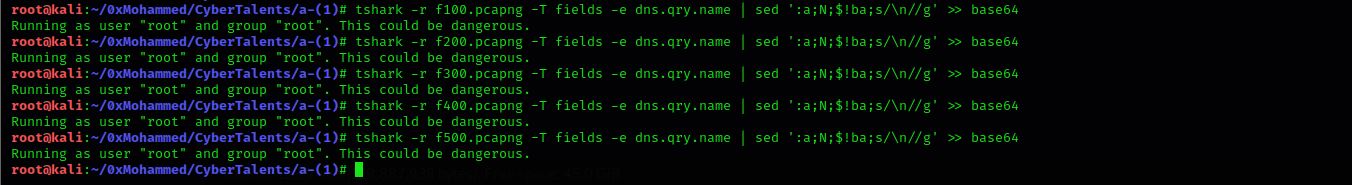
Looking at packets it contains just dns quieries with some base64 string each packet, so all we have to is to extract this strings decode it and get the output. Using this commandtshark -r >filename< -T fields -e dns.qry.name | sed ':a;N;$!ba;s/\n//g' - Step 4: Decoding outputs
Using base64 utilitybase64 -d filenamewe decoded the output and give us another wave file - Step 5: Getting flag
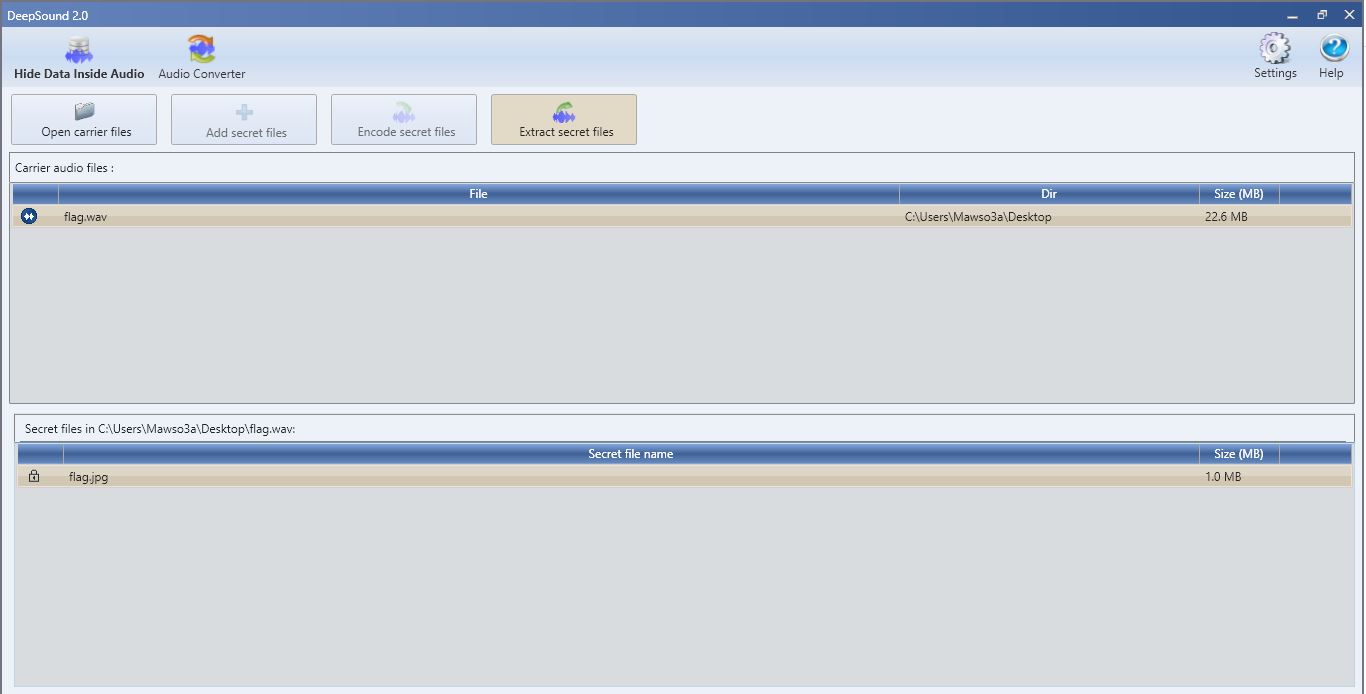
Going through usual process again of analysing wave file we found the flag using deepsoound tool inside an image called flag.jpg